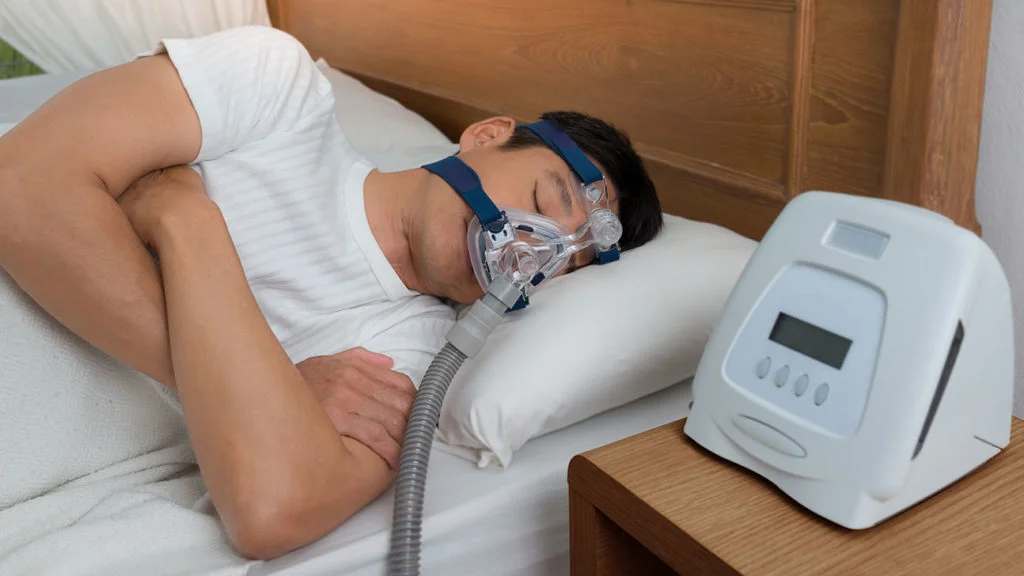
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These pauses, which can last from a few seconds to a minute, often occur multiple times per hour, leading to fragmented sleep and reduced oxygen levels in the body. Individuals with sleep apnea frequently experience excessive daytime sleepiness, headaches, difficulty concentrating, and even long-term health risks such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes. Timely diagnosis and effective management are essential to improve sleep quality and overall well-being. Accessing professional sleep apnea treatment Singapore ensures that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their specific condition.
Understanding the Causes of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can be classified into three main types:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common type, OSA occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, blocking the airway during sleep. Factors such as obesity, large tonsils, or a small jaw structure can increase the risk.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): Unlike OSA, CSA arises when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles controlling breathing. This type is often associated with heart conditions, stroke, or certain medications.
- Complex Sleep Apnea: Also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, this is a combination of OSA and CSA, requiring specialized management.
Identifying the type and underlying cause of sleep apnea is critical for determining the most effective treatment approach.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
For mild cases of sleep apnea, lifestyle modifications can be highly effective in reducing symptoms. Recommended strategies include:
- Weight Management: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can contribute to airway obstruction. Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the severity of sleep apnea.
- Sleep Positioning: Sleeping on the side instead of the back can prevent the tongue and soft tissues from blocking the airway.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the throat muscles, increasing the likelihood of airway collapse.
- Maintaining a Regular Sleep Schedule: Consistent sleep patterns can help regulate breathing and reduce the frequency of apnea episodes.
Incorporating these lifestyle adjustments often complements professional treatments, improving overall outcomes.
Medical Devices for Sleep Apnea
Medical devices are a cornerstone of sleep apnea management, particularly for moderate to severe cases. The most common options include:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Machines: CPAP is the gold standard for OSA. It delivers a steady stream of air through a mask, keeping the airway open during sleep.
- Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Machines: Similar to CPAP, BiPAP provides variable air pressure for inhalation and exhalation, often used in patients who cannot tolerate CPAP.
- Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs): These custom dental appliances reposition the lower jaw and tongue to prevent airway obstruction, offering an alternative for patients with mild to moderate OSA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP.
Professional guidance is essential for proper device selection, fitting, and monitoring to ensure effective treatment and comfort.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be considered for patients whose sleep apnea does not respond to non-invasive treatments. Surgical approaches aim to remove or reposition tissues that obstruct the airway or correct structural abnormalities. Common surgical interventions include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removal of excess tissue from the throat, including the uvula and soft palate, to widen the airway.
- Genioglossus Advancement (GA): Repositioning of the tongue muscle attachment to prevent airway collapse.
- Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): Surgical repositioning of the upper and lower jaw to enlarge the airway space.
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: Implantation of a device that stimulates the tongue muscle to maintain airway patency during sleep.
Surgical treatments are typically reserved for severe or refractory cases and require careful evaluation by a specialist.
Preventive Measures and Ongoing Care
Long-term management of sleep apnea includes regular monitoring and preventive strategies to minimize recurrence and complications. Patients are encouraged to:
- Attend routine follow-ups to assess treatment effectiveness
- Monitor weight and adopt a healthy lifestyle
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and sedatives that may worsen symptoms
- Use prescribed devices consistently and properly
- Maintain oral and dental health, particularly if using mandibular devices
A combination of professional care, lifestyle adjustments, and patient compliance ensures the best possible outcomes for managing sleep apnea.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a complex condition with potentially serious health implications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, exploring lifestyle changes, utilizing medical devices, and considering surgical options when necessary provides a comprehensive approach to management. Accessing professional sleep apnea treatment Singapore ensures accurate diagnosis and personalized care, helping patients achieve restful sleep, improved health, and a better quality of life. Early intervention and ongoing management are key to preventing complications and maintaining long-term wellness.